How To Get A Service Animal For Vertigo And Balance Disorder
What is a residue disorder?
A balance disorder is a condition that makes you feel unsteady or dizzy. If you are standing, sitting, or lying downwards, you might feel as if you are moving, spinning, or floating. If y'all are walking, yous might all of a sudden feel every bit if yous are tipping over.
Everyone has a airheaded spell now then, but the term "dizziness" tin hateful unlike things to different people. For 1 person, dizziness might hateful a fleeting feeling of faintness, while for another information technology could exist an intense sensation of spinning (vertigo) that lasts a long time.
About fifteen percent of American adults (33 1000000) had a rest or dizziness trouble in 2008. Balance disorders can be acquired past sure health conditions, medications, or a problem in the inner ear or the encephalon. A residual disorder can profoundly affect daily activities and cause psychological and emotional hardship.
What are the symptoms of a residue disorder?
If you take a balance disorder, your symptoms might include:
- Dizziness or vertigo (a spinning sensation).
- Falling or feeling as if y'all are going to fall.
- Staggering when you try to walk.
- Lightheadedness, faintness, or a floating sensation.
- Blurred vision.
- Confusion or disorientation.
Other symptoms might include nausea and airsickness; diarrhea; changes in heart rate and blood pressure; and fear, anxiety, or panic. Symptoms may come up and go over brusk time periods or last for a long time, and can lead to fatigue and depression.
What causes residuum disorders?
Causes of balance problems include medications, ear infection, a caput injury, or anything else that affects the inner ear or brain. Depression claret pressure level tin atomic number 82 to dizziness when you stand up too apace. Problems that touch the skeletal or visual systems, such as arthritis or heart muscle imbalance, can also cause rest disorders. Your risk of having balance bug increases equally you become older.
Unfortunately, many residue disorders offset all of a sudden and with no obvious crusade.
How does my trunk keep its balance?
Your sense of balance relies on a series of signals to your brain from several organs and structures in your torso, specifically your eyes, ears, and the muscles and touch sensors in your legs. The part of the ear that assists in balance is known equally the vestibular system, or the labyrinth, a maze-similar structure in your inner ear made of bone and soft tissue.
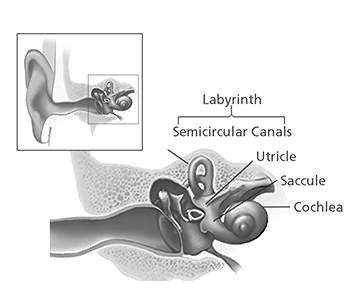
Structures of the balance organisation inside the inner ear
Source: NIH/NIDCD
Within the labyrinth are structures known as semicircular canals. The semicircular canals comprise three fluid-filled ducts, which form loops arranged roughly at right angles to ane another. They tell your encephalon when your caput rotates. Within each canal is a gelatin-like structure chosen the cupula [KEW-pyew-lah], stretched similar a thick sail that blocks off ane end of each canal. The cupula sits on a cluster of sensory hair cells. Each hair prison cell has tiny, thin extensions called stereocilia that beetle into the cupula.
When you plough your head, fluid inside the semicircular canals moves, causing the cupulae to flex or billow similar sails in the air current, which in plow bends the stereocilia. This bending creates a nervus bespeak that is sent to your encephalon to tell it which fashion your caput has turned.
Between the semicircular canals and the cochlea (a snail-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear) prevarication ii otolithic [oh-toe-LITH-ic] organs: fluid-filled pouches chosen the utricle [YOU-trih-cull] and the saccule [SACK-kewl]. These organs tell your encephalon the position of your head with respect to gravity, such as whether you are sitting up, leaning back, or lying down, as well as whatever management your head might be moving, such equally side to side, up or down, forward or backward.
The utricle and the saccule also have sensory pilus cells lining the floor or wall of each organ, with stereocilia extending into an overlying gel-like layer. Here, the gel contains tiny, dense grains of calcium carbonate called otoconia [oh-toe-CONE-ee-ah]. Any the position of your caput, gravity pulls on these grains, which then move the stereocilia to indicate your head's position to your brain. Any head movement creates a signal that tells your encephalon about the change in head position.
When you move, your vestibular organization detects mechanical forces, including gravity, that stimulate the semicircular canals and the otolithic organs. These organs piece of work with other sensory systems in your body, such every bit your vision and your musculoskeletal sensory system, to control the position of your trunk at balance or in motion. This helps you maintain stable posture and keep your remainder when you're walking or running. Information technology too helps you keep a stable visual focus on objects when your body changes position.
When the signals from any of these sensory systems malfunction, you tin can have problems with your sense of balance, including dizziness or vertigo. If y'all have additional problems with motor command, such as weakness, slowness, tremor, or rigidity, you can lose your power to recover properly from imbalance. This raises the gamble of falling and injury.
What are some types of balance disorders?
There are more than a dozen different residuum disorders. Some of the most common are:
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) or positional vertigo: A cursory, intense episode of vertigo triggered by a specific change in the position of the head. You might experience as if y'all're spinning when you bend downwardly to look under something, tilt your head to expect up or over your shoulder, or roll over in bed. BPPV occurs when loose otoconia tumble into one of the semicircular canals and bear on how the cupula works. This keeps the cupula from flexing properly, sending incorrect information nigh your caput's position to your brain, and causing vertigo. BPPV can result from a head injury, or can develop just from getting older.
- Labyrinthitis : An infection or inflammation of the inner ear that causes dizziness and loss of residuum. It is oftentimes associated with an upper respiratory infection, such as the influenza.
- Ménière's disease : Episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus (a ringing or buzzing in the ear), and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Information technology may exist associated with a alter in fluid volume within parts of the labyrinth, but the cause or causes are still unknown. For more data, read the NIDCD fact sheet Ménière's Disease.
- Vestibular neuronitis: An inflammation of the vestibular nerve that can exist caused by a virus, and primarily causes vertigo.
- Perilymph fistula: A leakage of inner ear fluid into the heart ear. It causes unsteadiness that usually increases with action, along with dizziness and nausea. Perilymph fistula can occur after a head injury, dramatic changes in air force per unit area (such equally when scuba diving), physical exertion, ear surgery, or chronic ear infections. Some people are born with perilymph fistula.
- Mal de Debarquement syndrome (MdDS): A feeling of continuously rocking, swaying, or bobbing, typically after an ocean cruise or other sea travel, or fifty-fifty after prolonged running on a treadmill. Usually the symptoms go abroad within a few hours or days later y'all attain state or finish using the treadmill. Severe cases, however, tin last months or fifty-fifty years, and the cause remains unknown.
How are residual disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a balance disorder is difficult. To find out if you have a balance problem, your primary md may suggest that you see an otolaryngologist and an audiologist. An otolaryngologist is a doctor and surgeon who specializes in diseases and disorders of the ear, olfactory organ, neck, and throat. An audiologist is a clinician who specializes in the function of the hearing and vestibular systems.
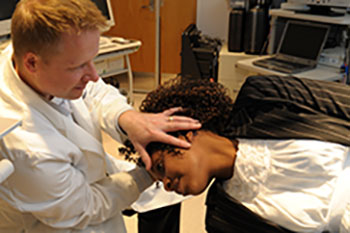
Dislodging otoconia using the Epley maneuver.
Source: NIH/NIDCD
Y'all may be asked to participate in a hearing examination, blood tests, a video nystagmogram (a test that measures heart movements and the muscles that control them), or imaging studies of your head and brain. Another possible test is chosen posturography. For this examination, you stand on a special movable platform in front end of a patterned screen.
Posturography measures how well you can maintain steady residue during different platform weather condition, such equally continuing on an unfixed, movable surface. Other tests, such equally rotational chair testing, brisk caput-shaking testing, or even tests that measure out eye or cervix muscle responses to cursory clicks of sound, may also exist performed. The vestibular system is complex, so multiple tests may exist needed to best evaluate the cause of your balance problem.
How are balance disorders treated?
The starting time thing an otolaryngologist volition exercise if you have a balance problem is make up one's mind if another health status or a medication is to blame. If so, your doctor volition treat the status, suggest a different medication, or refer you to a specialist if the condition is outside his or her expertise.
If yous have BPPV, your otolaryngologist or audiologist might perform a serial of simple movements, such as the Epley maneuver, to assist dislodge the otoconia from the semicircular canal. In many cases, i session works; other people need the procedure several times to relieve their dizziness.
If yous are diagnosed with Ménière'south disease, your otolaryngologist may recommend that yous brand some changes to your diet and, if y'all are a smoker, that you stop smoking. Anti-vertigo or anti-nausea medications may relieve your symptoms, but they tin too brand you drowsy. Other medications, such equally gentamicin (an antibiotic) or corticosteroids may exist used. Although gentamicin may reduce dizziness better than corticosteroids, information technology occasionally causes permanent hearing loss. In some severe cases of Ménière's disease, surgery on the vestibular organs may be needed.
Some people with a balance disorder may not be able to fully relieve their dizziness and will need to find ways to cope with information technology. A vestibular rehabilitation therapist tin aid you develop an individualized treatment program.
Talk to your doctor about whether it's safe to drive, and well-nigh ways to lower your take chances of falling and getting hurt during daily activities, such as when yous walk up or downwards stairs, utilise the bathroom, or exercise. To reduce your risk of injury from dizziness, avoid walking in the dark. Wear low-heeled shoes or walking shoes outdoors. If necessary, use a cane or walker and modify conditions at your home and workplace, such every bit calculation handrails.
When should I seek help if I think I have a balance disorder?
To help you decide whether to seek medical assistance for dizziness or balance bug, ask yourself the following questions. If yous answer "yes" to whatever of these questions, talk to your doctor:
- Practice I feel unsteady?
- Practise I feel as if the room is spinning around me, even for a very brief time?
- Practice I feel as if I'm moving when I know I'grand sitting or standing still?
- Do I lose my residuum and fall?
- Do I feel as if I'm falling?
- Do I feel lightheaded or as if I might faint?
- Practice I have blurred vision?
- Practice I ever experience disoriented—losing my sense of time or location?
How tin can I help my doctor make a diagnosis?
You can help your doc make a diagnosis and determine a treatment plan past answering the questions beneath. Be prepared to discuss this information during your appointment.
- The best manner I can draw my dizziness or balance problem is:
- Is there a spinning sensation, and if so, which way does the room spin?
- Is the dizziness/spinning caused past whatsoever specific motion or does information technology occur even when sitting or lying still?
- Are there any other symptoms that occur at the same time as the dizziness/spinning, such as hearing loss, tinnitus, a feeling of pressure level in one or both ears, or a headache?
- Does annihilation seem to help the dizziness/spinning?
- How oftentimes do I experience light-headed or have trouble keeping my residuum? How long practise the dizziness or spinning episodes last (seconds, minutes, hours, days)?
- Accept I ever fallen?
- When did I autumn?
- Where did I fall?
- Under what atmospheric condition did I fall?
- How oft have I fallen?
- These are the medicines I have. Include all prescription medications; all over-the-counter medicine, such equally aspirin, antihistamines, or sleep aids; and all vitamin supplements and culling or homeopathic remedies:
- Name of medicine or supplement: ______________________.
- How much (milligrams) _____ and how often (times) ______ per solar day.
- The condition I take this medicine for is: __________________________.
What research is being washed on balance disorders?
Scientists supported by the National Plant on Deafness and Other Advice Disorders (NIDCD) are studying brute ears to acquire if inner-ear structures that aid with balance merely are destroyed by aging, medications, infections, or trauma tin can anytime exist regrown in people with balance problems. Other NIDCD-supported scientists are testing vestibular prostheses—miniature devices that may exist worn outside the body or implanted into the ear to regulate the role of balance organs in the inner ear and ease dizziness. Some of these devices are existence tested on volunteers in clinical trials, and others are still being developed. Visit the NIH Clinical Research Trials and You website to read nearly these and other clinical trials that are recruiting volunteers.
NIDCD-funded scientists are also working to develop much-needed tests to appropriately diagnose balance disorders. Standardized tests will help doctors make up one's mind the best way to assistance individuals restore their sense of balance and quality of life. These tests will also assist us understand how many people suffer from rest disorders, and track whether the sense of balance is restored following treatment.
Where can I observe additional data about balance disorders?
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, residual, taste, smell, phonation, speech, and linguistic communication.
For more information, contact us at:
NIDCD Data Clearinghouse
1 Communication Avenue
Bethesda, MD 20892-3456
Cost-gratuitous voice: (800) 241-1044
Price-free TTY: (800) 241-1055
Email: nidcdinfo@nidcd.nih.gov
NIH Pub. No. 00-4374
December 2017
Source: https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/balance-disorders
Posted by: walkerthlent.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Get A Service Animal For Vertigo And Balance Disorder"
Post a Comment